Image Processing
Welcome
This site features documentation on the image processing and optimization routines available in SPIDAL.
A basic philosophy underlying SPIDAL is that many problems in AI-related domains (including machine learning, image understanding, computer vision, etc) can be posed and solved using one of a relatively small number of general techniques. Instead of re-inventing algorithms that are customized for a particular application, we advocate posing new problems in terms of general and abstract techniques. For example, many problems involving analyzing sequences can be posed as Hidden Markov Models, whether the sequences are sentences, positions of objects across time, audio signals, or protein sequences.
This view encourages separating applications, models, algorithms, and implementations to maximize generalization and code reuse. An application involves solving a particular domain-specific problem. Many such domain-specific tasks can be posed in terms of a model that precisely defines a mathematical problem to be solved. Different models may make different assumptions, trading off between simplicity and faithfulness to the original problem. An algorithm is a particular strategy for solving for unknown variables in that model. Different algorithms can be used to solve a given model, often with different trade-offs between accuracy and speed. An implementation is one particular set of source codes for executing an algorithm. Implementations may use heuristics or simplifications to improve practical results or decrease running time of an algorithm.
Contents
The goal of this site is to help choose the right model and algorithm abstractions for a given novel problem, and then apply SPIDAL codes to these new problems. Thus in addition to information about how to use the libraries themselves, we include background information about what these routines do, how they work, and when to use them, and show examples of their use on real problems.
You can use this resource in several different ways:
If you'd like to see how to apply SPIDAL algorithms to real problems, see Exemplar Applications.
If you'd like to learn more about a particular model, see Models.
If you'd like to learn more about a particular algorithm, see Algorithms.
Exemplar applications
3D Reconstruction of Polar Ice
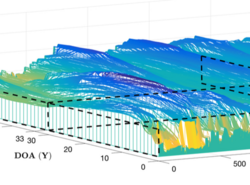
Reconstructs the three-dimensional surface of bedrock under polar ice using tomographic slices from ground-penetrating radar echograms.
- Research paper (IEEE International Conference on Image Processing 2017)
- Research project website
- Technologies: Image reconstruction, image recognition, discrete optimization, probabilistic inference
- Models: Markov Random Fields
- Algorithms: Loopy Belief Propagation, Tree-reweighted Message Passing
Segmentation of Radar Echograms
Segments location bedrock, ice, and air in radar echograms of polar ice.
- Research paper (IEEE International Conference on Pattern Recognition 2012)
- Research project website
- Technologies: Image segmentation, discrete optimization, probabilistic inference
- Models: Hidden Markov Models
- Algorithms: Viterbi
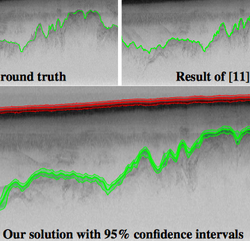
Identifies layer boundaries in radar echograms, including "soft" confidence bounds on layer locations.
- Research paper (IEEE International Conference on Image Processing 2014)
- Research project website
- Technologies: Image segmentation, discrete optimization, probabilistic inference
- Models: Hidden Markov Models, Markov Random Fields
- Algorithms: Markov Chain Monte Carlo
3D Reconstruction of Landmarks from Social Media images

Creates three-dimensional reconstructions of buildings and other landmarks from images downloaded from social media.
- Research paper (IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2013)
- Research project website
- Technologies: Discrete optimization, continuous optimization, image feature point extraction
- Models: Markov Random Fields, Non-linear Least Squares
- Algorithms: Loopy Belief Propagation, Levenberg-Marquardt, Scale Invariant Feature Transforms
Multi-modal Photo Clustering
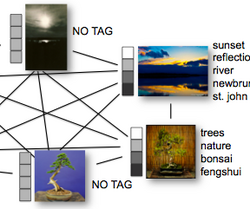
Clusters large-scale collections of images by combining visual, temporal, spatial, and textual features.
- Research paper (IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2014)
- Technologies: Clustering, discrete optimization, image feature extraction
- Models: Markov Random Fields, Bag-of-words
- Algorithms: Tree-reweighted Message Passing, K-means, Scale Invariant Feature Transforms
Organizes and visualizes social media images using multimodal features.
- Research paper (World Wide Web Conference 2009)
- Research project website
- Technologies: Clustering, image feature extraction
- Models: Bag-of-words, Support vector machines
- Algorithms: K-means, Mean shift
Photo segmentation

Produces multiple diverse candidate solutions for pixel-level semantic photo labeling.
- Research paper (Neural Information Processing Systems 2016)
- Technologies: Segmentation, deep learning, discrete optimization
- Models: Markov Random Fields, Deep Neural Networks
- Algorithms: Gradient Descent, Tree-reweighted Message Passing
Image recognition

Estimates where on Earth a photo was taken using visual, textual, and temporal features.
- Research paper (Book Chapter)
- Technologies: Recognition, deep learning, discrete optimization, continuous optimization, image feature extraction
- Models: Hidden Markov Models, Deep Neural Networks, Support Vector Machines, Bag-of-words
- Algorithms: Viterbi, Gradient Descent, K-means, k-nearest neighbors
Image captioning

Automatically produces diverse captions to describe an image.
- Research paper (ECCV Workshop 2016)
- Research project website
- Technologies: Deep learning, discrete optimization
- Models: Hidden Markov Models, Deep Neural Networks, Long-short Term Memories
- Algorithms: Viterbi, Gradient Descent
Algorithms
SPIDAL implementations are available for algorithms that solve various models and problems. The links below lead to more information about the algorithms, as well as source code and documentation.
Sequence model inference
- Viterbi algorithm for exact Maximum A Posteriori (MAP) inference
- Forward-Backward algorithm for exact marginal inference
- Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) for approximate MAP inference
Discrete optimization
- Loopy Belief Propagation for approximate optimization of Markov Random Fields
- Tree Reweighted Message Passing (TRW-S) for approximate optimization of Markov Random Fields
- Gibbs Sampling for approximate inference on Markov Random Fields
Continuous optimization
- Levenberg-Marquardt - non-linear least squares
- Gradient descent
Clustering and grouping
- K-means clustering
- Mean shift clustering
- Approximate all-pairs similarity search
- Deterministic Annealing
Dimensionality reduction
- Multidimensional Scaling (MDS)
Image processing and computer vision
- Unsupervised image segmentation
- Image alignment
- Edge detection
- Scale Invariant Feature Transform
Models
Sequence models
- Hidden Markov Models
- Long-short Term Memory models
Spatial models
Classification models
- Nearest neighbor
- Support Vector Machines
Regression models
- Non-linear least squares
- Deep Neural Networks
Image features
- Edges
- Interest points
- Bag of words models
